Updated Many Mac users today found, to their surprise, they are unable to print to their HP Inc printers.
- Check that your Mac is compatible. First, make sure your Mac can run Catalina. Apple provides a.
- The latest Code blocks v16.01 is not available for Mac OS because, as the team behind the IDE put it, they don't have developers to make one. So head on to codeblocks.org and download the version that is already available. You can directly download the bundle here. Let's get started with the installation.
Catalina is the latest build of Apple's Mac operating system, version 10.15. Released in October 2019, it's packed with plenty of new features Mac owners should love, like spreading cloud.
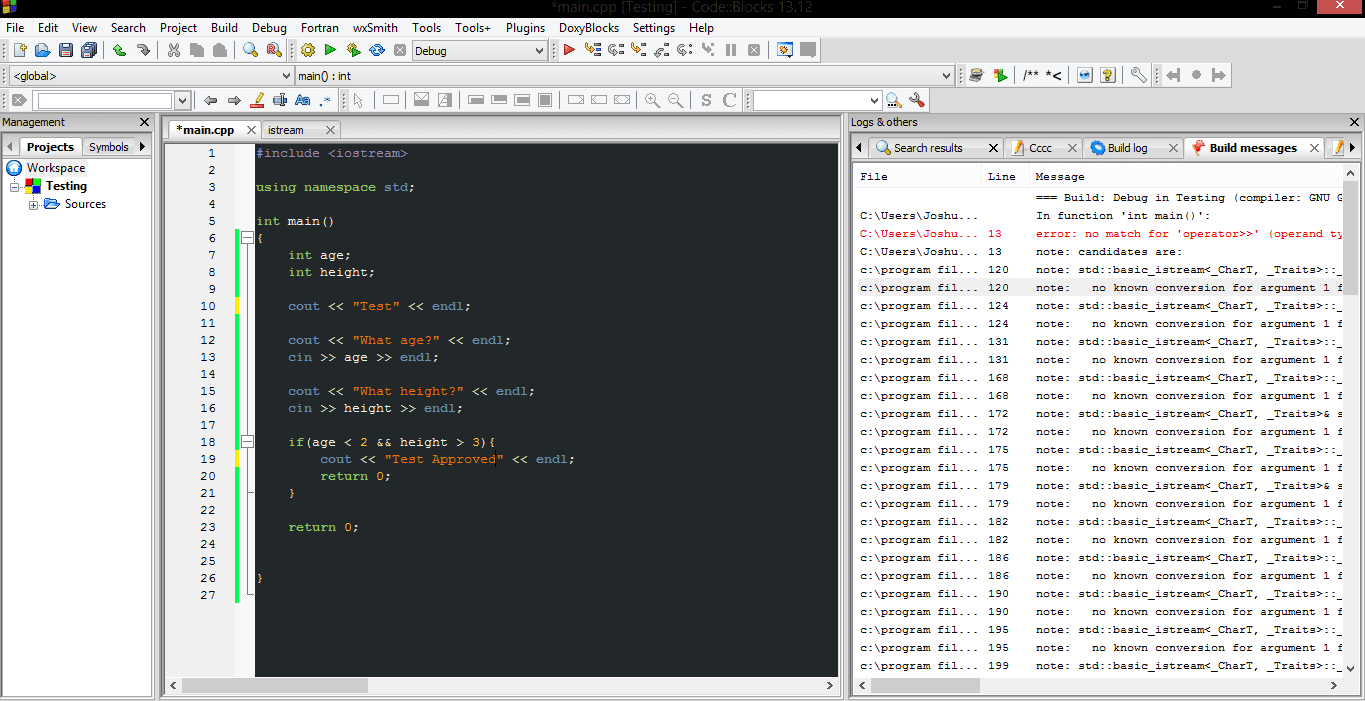
This is due to a code-signing snafu affecting macOS Catalina (version 10.15) and Mojave (10.14), specifically. HP's printer driver software is cryptographically signed with a certificate that macOS uses to determine whether the application is legit and can be trusted. However, that certificate was today revoked through an XProtect update, causing the software to be rejected by Macs.
XProtect is the mechanism Apple uses to inform Macs to no longer trust and run certain programs, and it does this by revoking their code-signing certificates. There is no central database of certs cancelled by XProtect, there's one for each OS version it seems, and Catalina and Mojave were selected in particular. Apple chose to revoke the HP driver cert, or perhaps was asked to do so by HP.
'No questions asked' Windows code cert slingers 'fuel trade' in digitally signed malware
READ MOREIn any case, HP's driver software no longer works on those two particular operating system flavors. Users are told when trying to print, for instance, that HP's application 'will damage your computer,' and are given the option to run it anyway or send it to the trash. Trying to continue just loops you back round to the error message, with no work done. Punters are also encouraged to report this 'malware' to Apple.
Unofficial workarounds for now include using AirPrint to an HP printer, or uninstalling the HP software and using a generic PostScript driver.
A Reg reader who tipped us off about the blunder told us he was able to jerry rig some IPP connectivity to get an older device to print: 'We had a handful of printers where macOS would print into the ether. Windows had no problem. I found some IPP trickery on macOS Catalina worked on an older HP4650.'
We had a handful of printers where macOS would print into the ether. Windows had no problem
Complaints from punters are building up on the Apple and HP support forums.
'Trying to open Printer Utility on MacOS 10.15.7 and I get a crash dump every time saying 'Code Signature Invalid' for the binary /Library/Printers/hp/Utilities/HP Utility.app/Contents/MacOS/HP Utility,' said one netizen.
'Yes, my Deskjet F4140 abruptly stopped working with both my Mac mini desktop AND my partner's AirBook,' complained another. 'The AirBook keeps insisting it's malware (it's not), while my desktop says the certificate has expired. Suddenly, HP and Apple are NOT playing well together! I've redownloaded and reinstalled the printer software TWICE now but nothing has changed, just the same message about HP Utility now missing. Our jobs depend on this printer, HP.'
Thomas Reed, director of Mac and mobile at Malwarebytes, tweeted to say his users were up in arms at the tech breakdown: 'We're seeing a significant influx of support cases where users are seeing macOS identify what appear to be legit processes as malware.'
Mac blogger Howard Oakley has some more background, here. 'You're seeing that [error] message because macOS is checking the signature on your HP printer software, and being told that its signing certificate has been revoked,' he observed.
Amazon's Music desktop app is also, weirdly enough, no longer working, either, it's reported.
Spokespeople for HP and Amazon were not available for immediate comment. Apple declined to comment. ®
Updated to add
The Register understands from sources familiar with the matter that HP Inc asked Apple to revoke its printer driver code-signing certificates. It appears this request backfired as it left users unable to print. A HP Inc spokesperson told us on Friday night:
We unintentionally revoked credentials on some older versions of Mac drivers. This caused a temporary disruption for those customers and we are working with Apple to restore the drivers. In the meantime, we recommend users experiencing this problem to uninstall the HP driver and use the native AirPrint driver to print to their printer.
These are instructions on how to build Code::Blocks under Apple Mac OS X.They have been tested under Mac OS X version 10.4 (PowerPC and Intel),and should work similarly on the newer Mac OS X 10.5 and 10.6 as well.
We will be building everything from scratch using the source code, andnot use any available package managers likeMacPorts,Fink,Gentoo orRPM.Packaging can be done later, once it has reached a more stable release.
Update: building for MacPorts can be found at the end of the document.
- 2Check Autotools versions
- 7Build wxWidgets
- 8Bundle library for Mac
- 10Build CodeBlocks from SVN
- 11Bundle application for Mac
- 11.1Way One: Mac OS (resource)
- 11.2Way Two: NeXT (bundle)
- 13Install with MacPorts
Install Developer Tools
If they didn't come bundled with Mac OS X, get the Xcode Tools (or Developer Tools for older Mac OS X) from http://developer.apple.com/tools/ or from your install disk.
This will install Apple versions of:
- http://www.gnu.org/software/gcc/ (GNU Compilers)
- http://www.gnu.org/software/gdb/ (GNU Debugger)
- http://www.gnu.org/software/make/ (GNU Make)
Apple regularly pulls all older links in order to promote newer Mac OS X, but all theold developer tools can be downloaded from ADC at http://connect.apple.com/
You need a (free) developer registration with Apple first, in order to log in there.For Mac OS X 10.4, you want (at least) Xcode 2.2, since earlier versions were buggy.
Check Autotools versions
Depending on your OS version, you might need to download and compile new versions of these:
- http://www.gnu.org/software/autoconf/ (GNU Autoconf)
- http://www.gnu.org/software/automake/ (GNU Automake)
- http://www.gnu.org/software/libtool/ (GNU Libtool)
Check what you have, with --version (note that GNU libtool is called 'glibtool' on Mac OS X)
Currently Code::Blocks requires versions:
- autoconf 2.50+
- automake 1.7+ (1.9+ needed in order to build the dist tarball)
- libtool 1.4+ (1.5.8+ highly recommended to get some bug fixes)
Automake example
For Mac OS X 10.4, you will only need an upgraded (local) installation of automake 1.9.x.
You can download 'automake-1.9.6.tar.gz' and configure and install it with something like:
Since it's now known as 'automake-1.9', it won't interfere with the regular 'automake'
If you would rather have the new version to be called when calling 'automake', let it install into /usr/local and put /usr/local/bin before /usr/bin in your PATH.
Libtool example
Download libtool source. The following instructions will overwrite your current version of libtool with the one you just downloaded.
Note that this will replace the system version of glibtool, which might have some compatibility issues with building other software.
FYI: Universal Binaries
If you are building for Mac OS X 10.4 or later, you might want to build 'Universal Binaries 'These are binaries that contain code for both PowerPC ('ppc' arch) and Intel ('i386' arch)
The basic flags that needs to be added are:
(You only need the sysroot parameter on PowerPC Macintosh, not on a Intel Macintosh)The '-arch i386 -arch ppc' is what tells the compiler to build a 'universal' (or 'fat') binary.
Usually it's easiest to build one version for 'powerpc-apple-darwin8',and one version for 'i686-apple-darwin8', and then merge them with 'lipo'
Some caveats:
- pre-compiled headers might fail with a 'no main' error. If they do, add a -c to only compile them
- when cross-compiling, tools like auto_revision might fail to build. copy these from a native build
- the Tiger compilers might crash from time to time, but that is only to be expected (it seems)...
See Technical Note TN2137: Building Universal Binaries from 'configure'-based Open Source Projects
FYI: Compilers
When building for older versions of the SDK, you want to make sure to use the same compiler.
Mac OS X 10.6 has GCC 4.2 as the default compiler, which won't work for the Mac OS X 10.4 SDK.
FYI: ANSI or UNICODE
For the moment we are using 'ANSI' (--disable-unicode, default) for Mac OS X 10.3 and earlier,and 'UNICODE' (--enable-unicode, optional) for Mac OS X 10.4 and later.
See http://www.wxwidgets.org/manuals/stable/wx_unicode.html#unicodeandansi
FYI: 32-bit or 64-bit
Code::Blocks currently uses wxMac (wxOSX/Carbon), which is 32-bit only. So it's not possible to build for 'x86_64'.

When Code::Blocks (and requirements) has been updated to use wxOSX/Cocoa, then a 64-bit version might be built too.
Build wxWidgets
Download the source code
Download the tarball for the wxMac release:
Apply necessary patches
Don't forget to apply any released patches!
Configure and (GNU) Make
note: the easiest way to build a Universal Binary with wxWidgets isthe new flag: --enable-universal_binary (you need wxWidgets 2.6.4+)
Install into Destination
Bundle library for Mac
To avoid having the Code::Blocks user having to compile or install wxWidgets themselves,we can bundle it with our application so that it is contained in the application bundle.This could also be done by statically linking wxWidgets, but with dynamic linking we canshare the wxWidgets library between all applications using wxWidgets (not just Code::Blocks)
Way One: Library (dynamic)
To bundle our shared library with the application, we include it in 'MacOS' and change the path:
@executable_path will be replaced with e.g. /Developer/Applications/CodeBlocks.app/Contents/MacOS
Way Two: Framework (bundle)
To bundle our framework with the application, we include it in 'Frameworks' and change the path:
This way it will first look in the framework path (-F), and then in for the shared library path (-L) as usual.
Install Subversion client
On Mac OS X 10.4, you need to install the Subversion (svn) program:
Note: you need SVN for the Code::Blocks revision scripts to work!
Build CodeBlocks from SVN
Download the source code
Apply necessary patches
For a list of all available patches, see:

You might need to convert line endings from DOS to Unix first.
Bootstrap with Autotools
You need to use the newer version of automake (see above), for the 'bootstrap'. (OS X 10.5 users may have recent enough autotools so they may not need to install them)
Mono Fix
If you have the Mono.framework installed, then it probably set up a symlink like:
Unless you have a 'proper' pkg-config installation the Code::Blocks configure will fail, so move this symbolic link aside.
Configure
Note: the easiest way to build a Universal Binary for Code::Blocks is to build once for PowerPC (-arch ppc) and once for Intel (-arch i386), and then merge them (with lipo) afterwards.
Note: You need to patch the location of the pre-compiled headers, or it will generate them in the same place for both arch.
Tiger Fix
There is a bug in the glibtool of Mac OS X 10.4, that fails to link C++ libs:
To work around this, you need to edit the generated 'libtool' script manually:
This bug has been fixed in GNU libtool 1.5.8 and later.
(GNU) Make
'nice' isn't strictly needed, it just makes the compile run at a lower process priority
For the Universal Binary build:
Install into Destination
'sudo' asks you for an admin password, in order to get install permissions
For the Universal Binary build:
Where 'lipomerge' is a custom shell script:
Bundle application for Mac
After building codeblocks in the regular Unix way, you need to bundle it with the iconsand various other info that it needs to make a regular stand-alone Macintosh application.
There are two ways of accomplishing this, old Mac OS-style resource or NeXT-style bundle.The old resources are handy while developing, while bundles are more suitable for release.
Note: You need to use either of these methods, or your application will launchin the background behind all other windows and will be unable to receive any events!
Way One: Mac OS (resource)
Handy while developing, as you don't need to create a whole bundle.
First we install the program to the PREFIX directory of your choice:
Note: on the Intel Macintoshes, the icon comes up as 'broken'(apparently it assumes that all apps with resforks are Classic)
Start the application with a small prefix shell wrapper like this:
You don't need the 'DYLD_LIBRARY_PATH' stuff,if you are installing to a system directory.
Common PREFIX Settings
When Code::Blocks (and requirements) has been updated to use wxOSX/Cocoa, then a 64-bit version might be built too.
Build wxWidgets
Download the source code
Download the tarball for the wxMac release:
Apply necessary patches
Don't forget to apply any released patches!
Configure and (GNU) Make
note: the easiest way to build a Universal Binary with wxWidgets isthe new flag: --enable-universal_binary (you need wxWidgets 2.6.4+)
Install into Destination
Bundle library for Mac
To avoid having the Code::Blocks user having to compile or install wxWidgets themselves,we can bundle it with our application so that it is contained in the application bundle.This could also be done by statically linking wxWidgets, but with dynamic linking we canshare the wxWidgets library between all applications using wxWidgets (not just Code::Blocks)
Way One: Library (dynamic)
To bundle our shared library with the application, we include it in 'MacOS' and change the path:
@executable_path will be replaced with e.g. /Developer/Applications/CodeBlocks.app/Contents/MacOS
Way Two: Framework (bundle)
To bundle our framework with the application, we include it in 'Frameworks' and change the path:
This way it will first look in the framework path (-F), and then in for the shared library path (-L) as usual.
Install Subversion client
On Mac OS X 10.4, you need to install the Subversion (svn) program:
Note: you need SVN for the Code::Blocks revision scripts to work!
Build CodeBlocks from SVN
Download the source code
Apply necessary patches
For a list of all available patches, see:
You might need to convert line endings from DOS to Unix first.
Bootstrap with Autotools
You need to use the newer version of automake (see above), for the 'bootstrap'. (OS X 10.5 users may have recent enough autotools so they may not need to install them)
Mono Fix
If you have the Mono.framework installed, then it probably set up a symlink like:
Unless you have a 'proper' pkg-config installation the Code::Blocks configure will fail, so move this symbolic link aside.
Configure
Note: the easiest way to build a Universal Binary for Code::Blocks is to build once for PowerPC (-arch ppc) and once for Intel (-arch i386), and then merge them (with lipo) afterwards.
Note: You need to patch the location of the pre-compiled headers, or it will generate them in the same place for both arch.
Tiger Fix
There is a bug in the glibtool of Mac OS X 10.4, that fails to link C++ libs:
To work around this, you need to edit the generated 'libtool' script manually:
This bug has been fixed in GNU libtool 1.5.8 and later.
(GNU) Make
'nice' isn't strictly needed, it just makes the compile run at a lower process priority
For the Universal Binary build:
Install into Destination
'sudo' asks you for an admin password, in order to get install permissions
For the Universal Binary build:
Where 'lipomerge' is a custom shell script:
Bundle application for Mac
After building codeblocks in the regular Unix way, you need to bundle it with the iconsand various other info that it needs to make a regular stand-alone Macintosh application.
There are two ways of accomplishing this, old Mac OS-style resource or NeXT-style bundle.The old resources are handy while developing, while bundles are more suitable for release.
Note: You need to use either of these methods, or your application will launchin the background behind all other windows and will be unable to receive any events!
Way One: Mac OS (resource)
Handy while developing, as you don't need to create a whole bundle.
First we install the program to the PREFIX directory of your choice:
Note: on the Intel Macintoshes, the icon comes up as 'broken'(apparently it assumes that all apps with resforks are Classic)
Start the application with a small prefix shell wrapper like this:
You don't need the 'DYLD_LIBRARY_PATH' stuff,if you are installing to a system directory.
Common PREFIX Settings
Local: PREFIX=/usr/local
System: PREFIX=/usr
MacPorts: PREFIX=/opt/local
Fink: PREFIX=/sw
Way Two: NeXT (bundle)
This does not involve resources, and is more relocatable.
Files needed:
- codeblocks.plist (generated, rename to 'Info.plist')
- codeblocks.sh (shell wrapper, rename to 'CodeBlocks')
- app.icns (icons are available in src/src/resources/icons)
The MacOS program will just be a shell wrapper that calls 'bin/codeblocks', like above.Traditionally the bundle would include Frameworks and Resources, but we'll just avoid thosehere and use the regular 'lib' and 'share/codeblocks' instead (just as with a regular install). These temporary directories are listed in italic below, they're not really used in bundles...
Setup a hierarchy like this, and copy the files from the regular build/install and the above file list to it:
The CodeBlocks application can now be moved with the Finder, and started up like a regular Mac application. (the nightly build includes a more advanced Info.plist and more icons - for also mapping all the files that the application can open, like source code and header files and such)
Proper Application Bundling
To avoid the shell wrapper, the binary can now be moved from 'bin/codeblocks' to 'MacOS/CodeBlocks'. Helper files are moved from 'share/codeblocks' to 'Resources'. The dynamic libraries are moved from 'lib' to 'MacOS':
To avoid having to use a DYLD_LIBRARY_PATH, we rename the shared libraries (with the install_name_tool program) from e.g. /usr/local/lib/ to @executable_path/:
The libraries can have their names changed using the -id parameter:
You also need to change all of the loadable bundles for the plugins:
You can check the result, what libraries/frameworks it links to, with:
Optionally you can then repeat the process, for the wx library too...
Here is a full script to do the job... It assumes to be executed at the same directory level as the CodeBlockSVN.app directory that will receive all the stuff... maybe enhanced but it is a first try that do work when packaging an OS X SVN build.
FYI: Darwin vs. Mac OS X
'Darwin is the UNIX technology-based foundation of Mac OS X.'
'Pure Darwin' here refers to the Open Source version of the OS:
Code Blocks Download Mac Os Catalina Dmg
- http://puredarwin.org/ or http://gnu-darwin.sourceforge.net/
(that is: Darwin using X11 instead of Aqua for the user interface)
Install with MacPorts
Install wxWidgets
You will need the wxWidgets library, install as port with:
If you want the X11/GTK version on Mac OS X, instead use:
Install Code::Blocks
After that is installed, you can install Code::Blocks with:
If you want the X11/GTK version on Mac OS X, instead use:
This will download the SVN trunk, and any dependencies:
Note: to upgrade from SVN, you need to uninstall first:
This is both because all SVN versions are numbered '0',but also due to a bug in the Code::Blocks build scripts.
Running +aqua (wxMac) version
After the build completes, you can start the program by:
Note that the wxMac application bundle in 'MacPorts'is just a wrapper, with symbolic links to /opt/local...
Running +x11 (wxGTK) version
The non-bundled wxGTK version is instead started with:
When running X11/wxGTK programs in Mac OS X, you can use'open-x11' to first start up X11.app and set up $DISPLAY:
